Ingredients You Can Trust
Our approach to key ingredients is led by the latest clinical science.
Why Caffeine, Not Clutter
At REV, we stick to what works. Caffeine is one of the most studied and proven performance enhancers on the planet—backed by decades of research. That’s why we don’t load our gum with trendy, unproven ingredients. No filler, no fluff—just clean, effective energy you can trust.

Increases Energy
Caffeine helps boost alertness and fight fatigue by stimulating the central nervous system.

Enhances Focus
It sharpens mental clarity and reaction time—ideal for work, workouts, or game time.

Improves Physical Performance
Caffeine increases endurance and power output, making it a go-to for athletes at all levels.

Supports Metabolism
It can elevate metabolic rate and fat oxidation, aiding in efficient energy use.
Why Caffeine, Not Clutter
At REV, we stick to what works. Caffeine is one of the most studied and proven performance enhancers on the planet—backed by decades of research. That’s why we don’t load our gum with trendy, unproven ingredients. No filler, no fluff—just clean, effective energy you can trust.

Increases Energy
Caffeine helps boost alertness and fight fatigue by stimulating the central nervous system.

Enhances Focus
It sharpens mental clarity and reaction time—ideal for work, workouts, or game time.

Improves Physical Performance
Caffeine increases endurance and power output, making it a go-to for athletes at all levels.

Supports Metabolism
It can elevate metabolic rate and fat oxidation, aiding in efficient energy use.

92% of customers
report noticeable improvements in energy or hydration with REV GUM
*Results based on a post purchase customer surve. Individual experiences may vary.
Science Backed Approach
From research and formulation to testing and production, everything we do is grounded in science. We source functional ingredients with purpose, validate their efficacy, and manufacture with precision to deliver a product built for high performance—trusted by athletes, adventurers, and high achievers alike

Proprietary Process
We utilize cutting edge innovative technology and processes to deliver a consistent high quality product.

Clinically studied
"Our formulas are built around clinically studied ingredients, selected for their proven effectiveness in enhancing energy, focus, and performance."

High-Quality Ingredients
We use only high-quality, functional ingredients—sourced for purity, potency, and backed by real science.
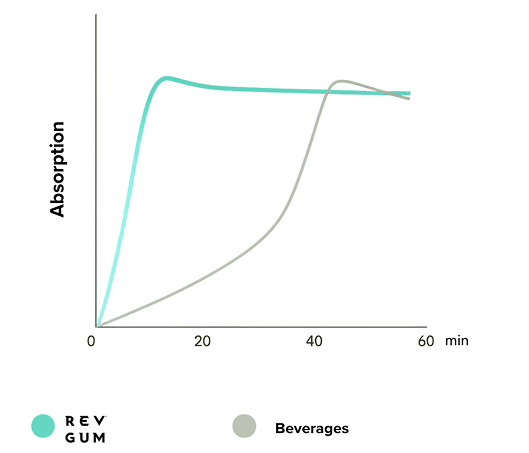
3x Faster Performance Than Our Competitors
Looking for a smart edge in your cardio performance? A new study shows that caffeine delivered via chewing gum can meaningfully improve 5 km run times. The research suggests that...
Real articleCaffeine Gum vs Capsules: Research-Based Insights This document summarizes key scientific findings on the absorption and bioavailability of caffeine administered in chewing gum versus traditional capsules, based on the study...
Real articleThe researchers gave caffeinated gum (400 mg caffeine, ≈ 4.1 mg/kg body weight) during a simulated half-time period to professional rugby players. They measured physiological (blood lactate, hormones like testosterone...
Real article
REV Energy Gum is a fast-acting, sugar-free chewing gum infused with caffeine, designed to give you an instant energy boost anytime, anywhere.
The caffeine is absorbed in the mouth by our natural salivation process. As soon as a piece of REV hits your tongue, the boost is already in motion!
Absolutely! REV GUM is formulated for daily use, with each piece containing a controlled dose of caffeine. Just be mindful of your total caffeine intake throughout the day.
One piece of REV Energy Performance Strength contains 60mg of caffeine—about a shot of espresso. Chew one for a quick pick-me-up or two if you need an extra boost, but don’t exceed your daily caffeine limit!
REV Electrolyte Gum is a fast-acting chewing gum infused with essential electrolytes to help replenish and keep you going strong—whether you're sweating it out or just need a refresh. No sugar, no mess, just chew and recharge.
Electrolytes are absorbed in the mouth by our natural salivation process. As soon as a you start chewing, the boost is already in motion!
Yes!
Each stick contains 64mg of Potassium or about 12oz of gatorades worth. Chew one or two for a quick electrolyte boost or more if needed!
Nope! REV Electrolyte Gum is completely caffeine-free—just pure electrolyte replenishment to help keep you hydrated and performing at your best.
Yes! We offer free standard shipping on all U.S. orders over $30.
We typically ship via USPS and other major carriers to get your Rev to you quickly and reliably.
Yes. At checkout, you’ll see available expedited options based on your location.
Sometimes carriers run into delays. If your package hasn’t shown up after the expected window, email us at support@chewrevgum.com and we’ll help sort it out.
Not at the moment — carriers don’t guarantee specific delivery windows. But you’ll always get tracking updates once your order ships.
If your order hasn’t shipped yet, reach out right away at support@chewrevgum.com and we’ll update it. Once it’s shipped, we can’t guarantee changes.
Yes — we do ship to PO Boxes and APO/FPO addresses in the U.S.
Not right now. All orders are shipped directly to you.
Yes! Rev Gum ships internationally. Shipping rates and delivery times are calculated at checkout depending on your country.
Check around your delivery area, with neighbors, or your building’s front desk. If it doesn’t turn up within 48 hours, email us at support@chewrevgum.com and we’ll help.
International orders usually take 7–21 business days depending on your country and customs clearance.
We accept all major credit cards, PayPal, Google Pay, and Apple Pay (if available).
Not currently. We handle all orders online to keep things fast, secure, and trackable.
Once your order ships, you’ll receive an email with tracking details. Use that to follow your package’s journey.
For U.S. orders: typically 1–3 business days. For international orders: usually 2–4 business days.
If your order hasn’t shipped yet, email us ASAP at support@chewrevgum.com with the corrected address and order number. After shipping, changing the address may not be possible.
Yes — but only if it hasn’t shipped yet. Reach out quickly at support@chewrevgum.com with your order details and we’ll try to stop it.
If it hasn’t shipped, we might be able to modify your order (flavor swap, quantity). Contact us immediately and we’ll see what we can do.
If you're not satisfied, we’ve got you. Within 30 days of delivery, contact support@chewrevgum.com with your order info and reason. Unopened items in original condition are eligible. Return shipping costs may apply.
Your subscription renews on the same day each period (monthly, etc.). You’ll be charged automatically unless canceled. You can pause, skip, or cancel at any time before the next shipment.
Sometimes demand outpaces supply or shipments are delayed. If something you ordered is on backorder, we’ll notify you with options (refund, wait, substitute).
















